| Author | Journal | Title |
|---|---|---|
| Kimoto et al. (2004) | Microbiol. Immunol. 48:75-82. | New Lactococcus strain with immunomodulatory activity: enhancement of Th1-type immune response. |
| Kimoto-Nira et al. (2007) | Br. J. Nutr. 98: 1178-1186. | Anti-aging effect of a lactococcal strain: analysis using senescence-accelerated mice |
| Kimoto-Nira et al. (2009) | Int. J. Food Microbiol. 129:321-324. | Inhibition of leukotriene B4 production in murine macrophages by lactic acid bacteria. |
| Kimoto-Nira et al. (2010) | Milchwissenschaft 65: 421-424. | Comparison of the anti-aging potential of Lactoccocus lactis strains and determination of the required feeding period for senescence-accelerated mouse. |
| Kimoto-Nira et al. (2012) | J. Nutr. Sci. 1:e18. | Oral intake of heat-killed cells of Lactococcus lactis strain H61 promotes skin health in women. |
| Kimoto-Nira et al. (2012) | J. Dairy Sci. 95:2863-2871. | A derivative of Lactococcus lactis strain H61 with less interleukin -12 induction has a different cell wall. |
| 木元ら(2012) | 日本畜産学会報83:307-313. | ヒトの肌の状態に対するLactococcus lactis H61の摂取効果ー年齢層別解析ー |
| 鈴木ら(2013) | New Diet Therapy. 29(1):23-30. | 乳酸菌Lactococcus lactis ssp. cremoris H61 含有ヨーグルトの継続摂取が女子大学生の肌、便通、体調に及ぼす影響 |
| Kimoto-Nira et al. (2014) | J. Dairy Sci. 97:5898-5903. | Effects of ingesting fermented milk by using Lactococcus lactis H61 on skin health in young women: A randomized double-blind study. |
| Kimoto-Nira et al. (2014) | J. Food Prot. 77:1161-1167. | Altered superoxide dismutase activity by carbohydrate utilization in a Lactococcus lactis strain. |
| Kimoto-Nira et al. (2015) | JARCP 4 :109-115. | Effects of ingesting milk fermented by Lactococcus lactis H61 on skin properties and health biomarkers in middle-aged women: a randomized, double-blind study. |
| Oike et al. (2016) | Sci. Rep. 6:23556. | Dietary intake of heat-killed Lactococcus lactis H61 delays age-related hearing loss in C57BL/6J mice. |
| 木元・守谷(2016) | 日本ペット栄養学会誌、19: 1-7. | Lactococcus lactis H61の投与によるイヌのエイジングレベルの改善の可能性 |
| 木元ら(2017) | ミルクサイエンス、66(1):1-7 | 夏季におけるLactococcus lactis H61含有ヨーグルトの摂取が中高年女性の肌及び体調に及ぼす影響 |
| 兼松ら(2017) | Bull.NARO, Livest.& Grassl. Sci.17:1-6. | ラクトコッカス ラクティスH61加熱死菌が子ブタの免疫系へ及ぼす影響. |
| Kimoto-Nira (2018) | Anim. Sc.i J. 89: 835-842. | New lactic acid bacteria for skin health via oral intake of heat-killed or live cells. |
| 木元(2018) | 日本乳酸菌学会誌、29:69-78 | Lactococcus lactis H61の老化抑制効果と作用機構の解明に向けて |
| Suzuki et al. (2022) | Int. J. Ana.l Bio-Sci Vol. 10, 33-41. | Lactococcus lactis subsp. cremoris H61 improved iron status in male distance runners |
| Takaragawa et al. (2022) | Nutrients 2022, 14, 3144. | Heat-Killed Lactococcus lactis subsp. cremoris H61 Altered the Iron Status of Young Women: A Randomized, Double-Blinded, Placebo-Controlled, Parallel-Group Comparative Study |
| Sato et al. (2024) | Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 10648 | Novel indirect antioxidant activity independent of Nrf2 exerted by lactic acid bacteria |
| 特許番号 | 発明の名称(共同出願人) |
|---|---|
| 特許第5783648号 | 乳酸菌を利用したメラニン産生抑制用又は育毛・発毛用皮膚外用剤 |
| 特許第5958983号 | 乳酸菌を利用した育毛・発毛用皮膚外用剤 |
| 特許第7144811号 | 鉄栄養状態改善剤(順天堂大学、東亜薬品工業) |
| 特許第7252606号 | 乳酸菌検出プライマーセットおよび該プライマーセットを用いた検出方法 |
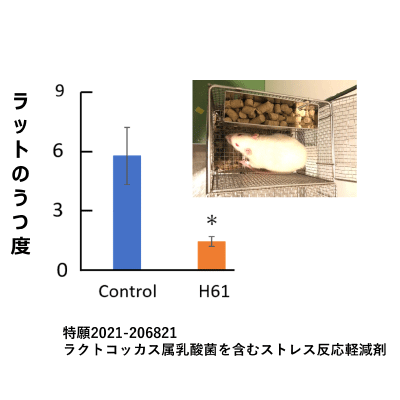
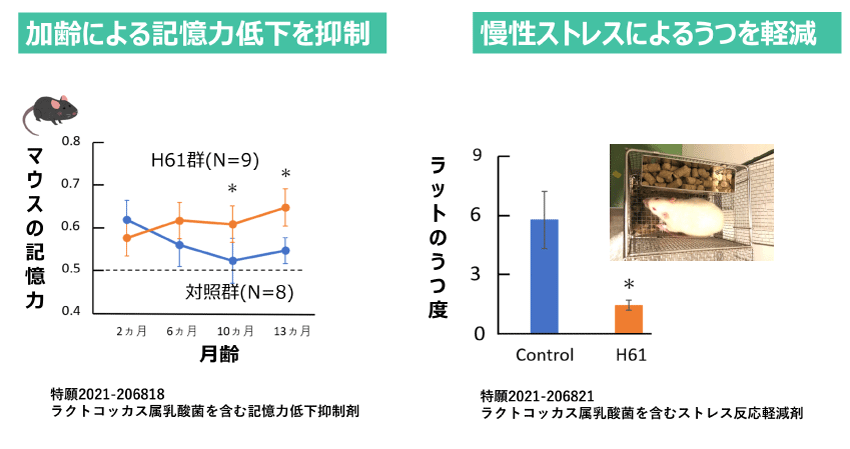
| 特願2021-206821 | ラクトコッカス属乳酸菌を含むストレス反応軽減剤 |
| 特願2021-206818 | ラクトコッカス属乳酸菌を含む記憶力低下抑制剤 |
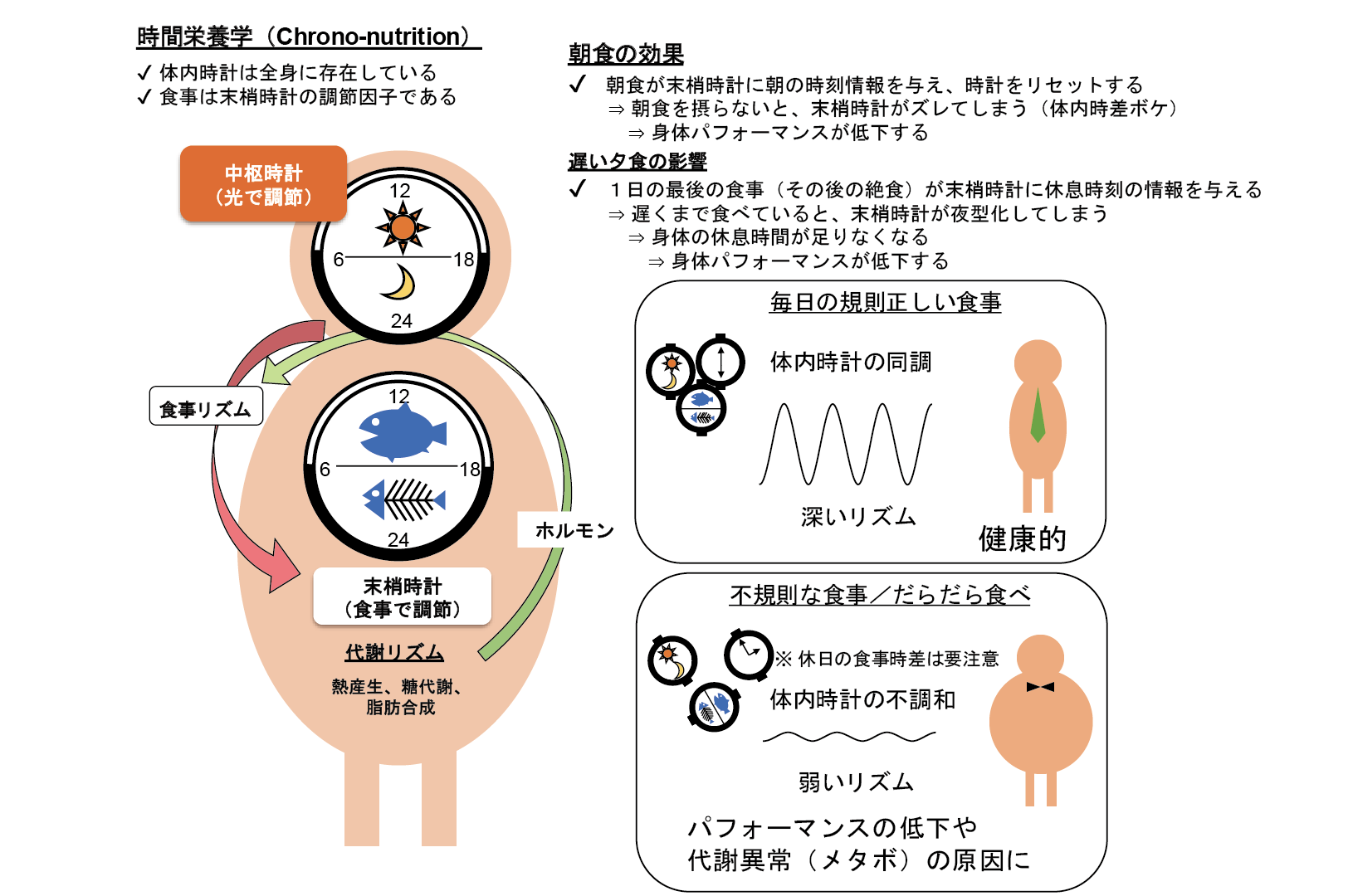
時間栄養学は、体内時計のはたらきを取り入れた栄養学です。これまでの栄養学は1日あたりの食事量を基準としますが、時間栄養学では、いつ食べるかが重要になります。わたしたちの身体は24時間リズムで周期的に変化しており、同じものを食べても、朝に食べるか夜に食べるかで、その意味合いも変わってしまうのです。
たとえば、筋肉の維持には、朝のたんぱく質シグナルが効果的です。また、メタボ対策には夜遅い時間の食事を減らすことが重要であり、血糖値対策には朝の食物繊維や間食が有効です。また、腸内細菌叢にも24時間リズムがあり、腸活にも適した時間があると考えられます。
健康な食生活のための時間栄養学の実践ポイントは、
ポリフェノール、野菜、果物、乳酸菌、ω3脂肪酸、健康オイル、抗酸化物質、ペプチド、アミノ酸、核酸、ビタミンなど100素材以上
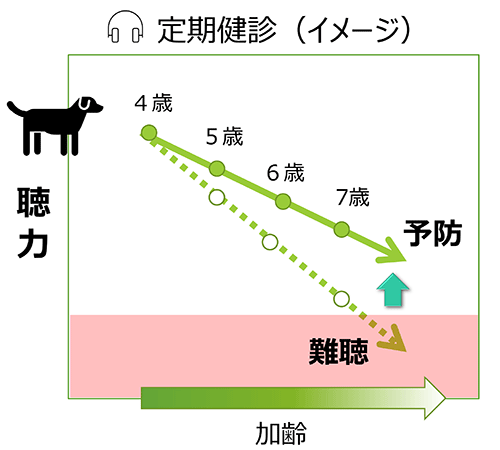
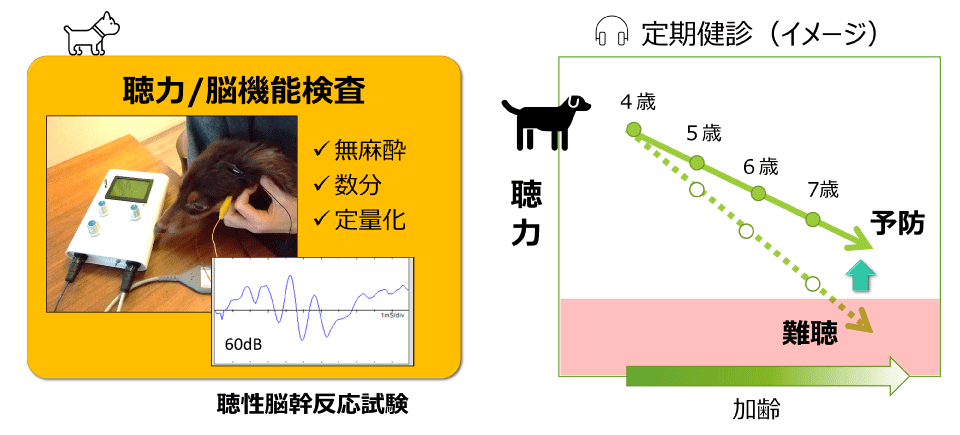
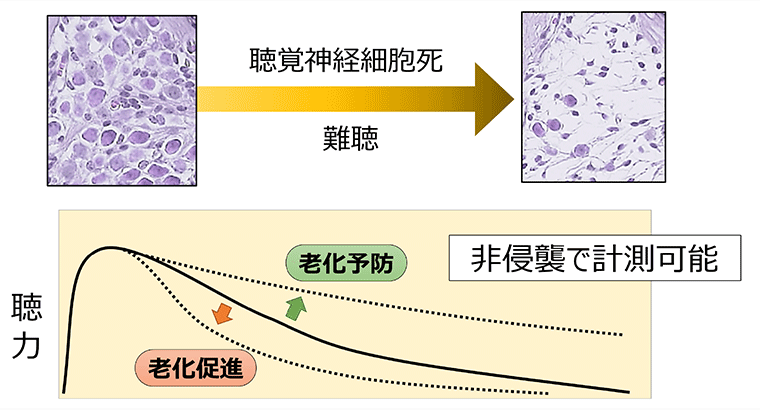
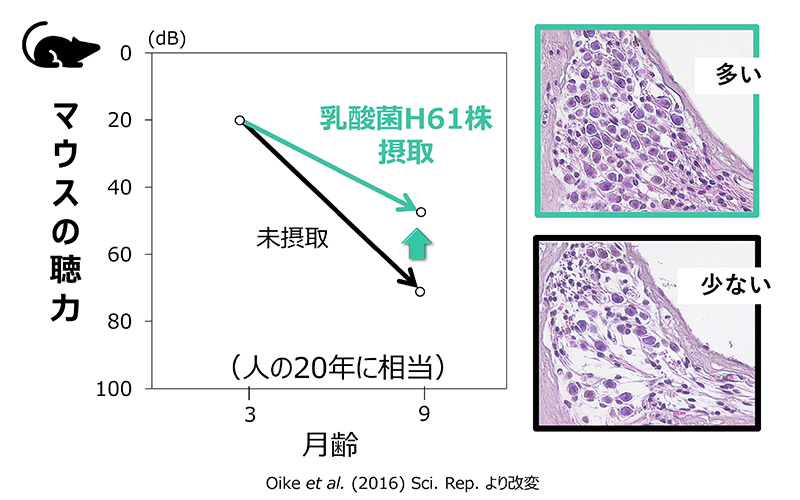
⇒ 乳酸菌H61株に高い難聴予防効果
難聴予防に関する研究資料(リンク先は農研機構HP内)
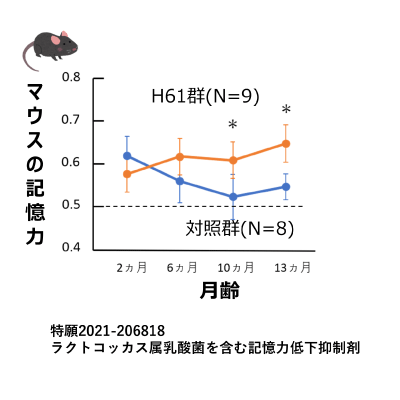
加齢による記憶力低下を抑制
慢性ストレスによるうつを軽減